Recycling in Germany
- Color-Coded Bins: Germany utilizes a color-coded bin system for recycling.
- Deposit System: Many beverage containers in Germany come with a deposit (“Pfand”) to encourage recycling.
- Glass Recycling: Glass containers without a deposit are recycled in color-coded recycling bins.
- Biodegradable Waste: The brown bin (“Biomüll”) is for biodegradable goods, processed into biogas & compost.
- High Estimated Recycling Rate: Germany boasts high recycling rates, with approximately 68 percent of packaging waste being recycled, surpassing the EU target of 55 percent.
Sorting Trash: The Key to Reduce, Reuse & Recycle
Germany’s waste production is substantial, emphasizing the importance of efficient recycling and waste management practices to mitigate environmental impact. Recycling is a well-established and highly effective system that plays a crucial role in the country’s waste management strategy. According to the Federal Statistical Office, there has been a clear rise in recycling rates since 2002, with the recycling rate for municipal waste reaching 65 percent for the first time in 2012. Numerous localities offer recycling depots where residents can dispose of certain materials and items like electronics, hazardous materials, and large items.
The German approach to recycling municipal waste emphasizes the importance of properly sorting trash to maximize the recovery of valuable materials and minimize waste sent to landfills. This commitment to recycling is evident in the meticulous sorting requirements for different types of waste, which are facilitated using color-coded bins and clear labeling. Understanding how to sort trash correctly is essential for residents and visitors alike, as it contributes to environmental sustainability and ensures compliance with German waste separation and waste disposal regulations.
Cracking the Code: Germany’s Color-Coded Bins
Germany’s waste management system is known for its efficiency and sustainability, highlighted by the use of five standard color-coded recycling bins. Each bin serves a specific purpose in the recycling process, emphasizing the country’s commitment to environmental stewardship. Understanding the role of each recycling bin is essential for residents and visitors alike, as proper use contributes to the success of Germany’s recycling efforts. In the following paragraphs, we will explore each bin type in detail.
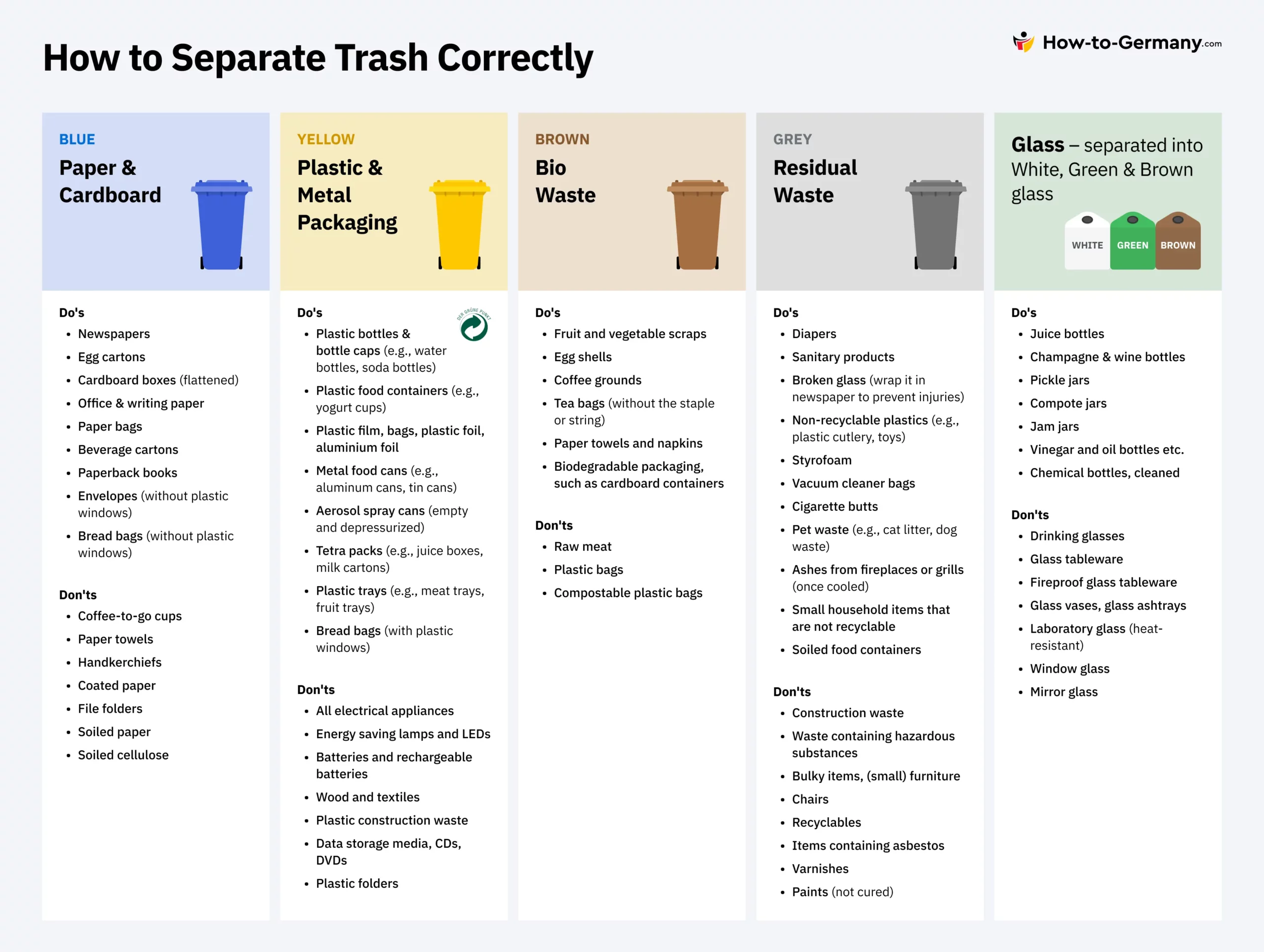
Blue Bin
he blue bin (Blaue Tonne) in Germany is designated for paper and cardboard recycling. It is important to note that plastic bags should not be used in the blue bin, as they can contaminate the recycling process. To facilitate recycling, cardboard boxes should be flattened before placing them in the blue bin. These measures help ensure the efficient processing of paper waste and cardboard waste, contributing to Germany’s sustainable waste management practices.
Here are some examples of items that can be disposed of in the blue bin, and which not:
- Newspapers
- Egg cartons
- Cardboard boxes (flattened)
- Office & writing paper
- Paper bags
- Beverage cartons
- Paperback books
- Envelopes (without plastic windows)
- Bread bags (without plastic windows)
- Coffee-to-go cups
- Paper towels
- Handkerchiefs
- Coated paper
- File folders
- Soiled paper
- Soiled cellulose
Yellow Bin or Orange Bin
The yellow bin or orange bin (Wertstofftonne) in Germany is used for recycling plastic containers and metal packaging with the Grüner Punkt logo. The yellow bin is crucial for the recycling of packaging materials, ensuring that they are properly sorted and processed. Items such as plastic bottles and packaging with the Grüner Punkt symbol should be placed in this bin.
Here are some examples of items that can be disposed of in the yellow bin:
- Plastic bottles & bottle caps (e.g., water bottles, soda bottles)
- Plastic food containers (e.g., yogurt cups)
- Plastic film, bags, plastic foil, aluminium foil
- Metal food cans (e.g., aluminum cans, tin cans)
- Aerosol spray cans (empty and depressurized)
- Tetra packs (e.g., juice boxes, milk cartons)
- Plastic trays (e.g., meat trays, fruit trays)
- Bread bags (with plastic windows)
- All electrical appliances
- Energy saving lamps and LEDs
- Batteries and rechargeable batteries
- Wood and textiles
- Plastic construction waste
- Data storage media, CDs, DVDs
- Plastic folders
The Grüner Punkt, which translates to “Green Dot” in English, is a symbol used in Germany and several other European countries to indicate that a fee has been paid for the recycling of packaging materials. It does not necessarily mean that the packaging is recyclable, but rather that the manufacturer has fulfilled its obligation to participate in a recycling system. The Grüner Punkt symbol encourages consumers to recycle in Germany and helps fund the recycling infrastructure. Usually, items with the green dot can be disposed of in the yellow bin.
Brown Bin
The brown bin (Biomüll) in Germany is specifically designated for biodegradable waste, such as food scraps and garden waste. This waste is processed to produce biogas and compost, which are valuable resources for energy production and soil enrichment. To ensure the quality of the compost and biogas, it is important not to use plastic or biodegradable bags in the brown bin; only paper bags should be used for disposal.
After the holiday season, Christmas trees in every German city are collected in January for recycling. To participate, residents can refer to their city’s trash & waste collection calendar, also known as the “Abfuhrkalender,” to find the specific collection dates. Typically, all that’s required is to place the tree next to the street for pickup.
The brown bin is used for disposing of various biodegradable waste, including:
- Fruit and vegetable scraps
- Egg shells
- Coffee grounds
- Tea bags (without the staple or string)
- Paper towels and napkins
- Biodegradable packaging, such as cardboard containers
- Raw meat
- Plastic bags
- Compostable plastic bags
Germany’s dedication to sustainability goes beyond recycling, encompassing a broader environmental mindset that guides municipal practices. Many cities encourage composting by supplying households with compost bins. This holistic approach to waste management yields nutrient-rich compost for gardens and farms, highlighting Germany’s commitment to environmental responsibility at all levels.
Grey Bin
The grey bin (Restmüll) in Germany is designated for disposing of non-recyclable waste that cannot be sold, donated, or recycled. This includes items such as certain types of packaging, hygiene products, and non-recyclable plastic waste. It is significant to note that certain items, e.g., hazardous waste, such as paints, oils, batteries and electronics, should not be disposed of in the grey bin.
Specific items e.g., Paints, oils, and lacquers can be disposed of at hardware stores. Major retailers such as Bauhaus, Hellweg, Hornbach, and OBI typically accept these items for proper disposal. This ensures that these potentially hazardous materials are handled and disposed of safely, preventing harm to the environment and public health. Customers can inquire with the store about their specific disposal process for these items.
Here are some examples of items that should be disposed of in the grey bin:
- Diapers
- Sanitary products
- Broken glass (wrap it in newspaper to prevent injuries)
- Non-recyclable plastics (e.g., plastic cutlery, toys)
- Styrofoam
- Vacuum cleaner bags
- Cigarette butts
- Pet waste (e.g., cat litter, dog waste)
- Ashes from fireplaces or grills (once cooled)
- Small household items that are not recyclable
- Soiled food containers
- Construction waste
- Waste containing hazardous substances
- Bulky items, (small) furniture
- Chairs
- Recyclables
- Items containing asbestos
- Varnishes
- Paints (not cured)
Glass Recycling Bins
Glass bins (Glasiglus) in Germany are designated for glass containers and glass bottles that do not have a deposit (Pfand). In Germany, there is no need to clean glass containers before recycling them. If your house or apartment building does not have glass bins, you can find them in your neighborhood.
Incandescent and fluorescent light bulbs should be disposed of in glass bins. Energy-saving light bulbs can be taken to a hardware store or recycling center for disposal, while neon lights should be taken to a hardware store or recycling center for proper disposal.
There are three types of bins for different coloured glass:
- Braunglas bin: brown glass
- Grünglas bin: green, red, and blue glass
- Weißglas bin: transparent glass resp. white glass
Proper use of these bins helps ensure that glass is recycled efficiently, reducing the need for new glass production and conserving resources.
- Juice bottles
- Champagne & wine bottles
- Pickle jars
- Compote jars
- Jam jars
- Vinegar and oil bottles etc.
- Chemical bottles, cleaned
- Drinking glasses
- Glass tableware
- Fireproof glass tableware
- Glass vases, glass ashtrays
- Laboratory glass (heat-resistant)
- Window glass
- Mirror glass
Additional Recycling Bins: Beyond the Basics
In addition to standard recycling bins, Germany also features other types of recycling facilities to promote responsible waste disposal. These include bottle return machines (Pfandautomat) for containers with a deposit, battery bins, and electronics recycling bins.
Bottle Return Machines
Bottle return machines (Pfandautomat) in Germany are specifically designed for containers with a deposit (Pfand), such as plastic and glass bottles. These machines are a common sight in most supermarkets, typically located near the entrance for convenience. They play a crucial role in encouraging recycling by providing a simple and efficient way for consumers to return their empty containers and receive their deposit back. Additionally, these machines help reduce littering and promote a more sustainable approach to waste management.
Electronics Recycling Bins
Electronics bins (Elektroschrott-Container) in Germany are specifically designated for used electronics and objects bearing the WEEE logo, indicating they fall under the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment directive. These bins are typically located in electronics stores, hardware stores, and some supermarkets, providing a convenient drop-off point for old or broken electrical appliances and electronic devices. Proper disposal of electronics is crucial to prevent hazardous materials from contaminating the environment, making these bins an essential part of Germany’s sustainable waste management practices.
The WEEE logo stands for Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment. It is a symbol used in the European Union to indicate that a product falls under the scope of the WEEE Directive. This directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste by promoting the reuse, recycling, and recovery of such products. Products bearing the WEEE logo should be disposed of separately from regular household waste and taken to designated collection points for proper recycling and disposal.
Battery Recycling Bins
Battery recycling bins (Altbatterien-Container) in Germany are specifically designated for used batteries and are typically found in most supermarkets, electronics stores, and hardware stores, conveniently located near the entrance. In addition to these locations, popular retailers like Rossmann and dm also offer battery recycling services, making it even more accessible for consumers to dispose of their used batteries responsibly.
FAQ: Recycling
In Germany, you can recycle batteries by taking them to designated collection points. Many supermarkets, electronics stores, and recycling centers have collection bins for used batteries. You can also return them to the place where you purchased them, even if you didn’t buy them there originally. It’s important to recycle batteries properly to prevent environmental contamination.
In Germany, the federal government has implemented several measures to improve waste separation, recycling, and save money on waste disposal. These include:
- Education and awareness campaigns are conducted to inform citizens about the importance of waste separation and how to do it correctly.
- Recycling bins for paper, plastic, bio-waste, and residual waste are provided to households.
- Collection systems are set up for specific types of waste like electronics and batteries.
- Legislation requires proper waste separation and imposes fines for non-compliance.
- Some municipalities offer incentives for proper waste separation.
- The government invests in recycling infrastructure to process separated waste efficiently.
In Germany, almost everything can be disposed of in a recycling bin for later re-use.
The German government saves a significant amount of money through implementing waste separation and recycling. By reducing the amount of waste that needs to be landfilled or incinerated, the government avoids costly disposal fees. Additionally, the revenue generated from selling recyclable items and materials further offsets waste management costs.